Department Process Engineering
Flotation instead of sedimentation for mechanical and biological treatment
Projekt HydroNET: Flotation instead of sedimentation - modular approach for small and medium WWTP
The HydroNet Project aims for the replacement of the sedimentation stage from a municipal wastewater treatment plant by dissolved air flotation.
Primary and secondary sedimentation demands similar space than the activated sludge tanks. In order to develop a space-saving modular and compact small sewage treatment plant, it is necessary to reduce the space of the primary and secondary clarifier.
The replacement of the clarifier through a primary and a secondary flotation unit creates several advantages:
- Significant reduction of treatment time and reduction of installation surface and volume.
- Combination of grid/oil trap and primary sedimentation in the pre-flotation.
- Possibility to increase the return sludge concentration in case of higher hydraulic loads.
The developing of a control system allows us to have direct influence on the flotation process. In contrast to the sedimentation system it is possible to change the flotation parameters to get a faster separation of sludge and treated wastewater and a higher concentration of the sludge.
Sludge thickening through Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF)
In an air flotation unit, air is dissolved under pressure in the liquid to be treated (30% recycle of oversaturated effluent). The liquid becomes supersaturated as the pressure is released, and the air in excess of what can be dissolved at atmospheric pressure generates small bubbles 10-100 µm in diameter. They collide with suspended solids and become attached by adhesion, entrapment, or adsorption. The floc- bubble conglomerate rise to the surface forming a “scum”, which is removed by skimmers. The clear liquid can then be withdrawn from the bottom of the tank.
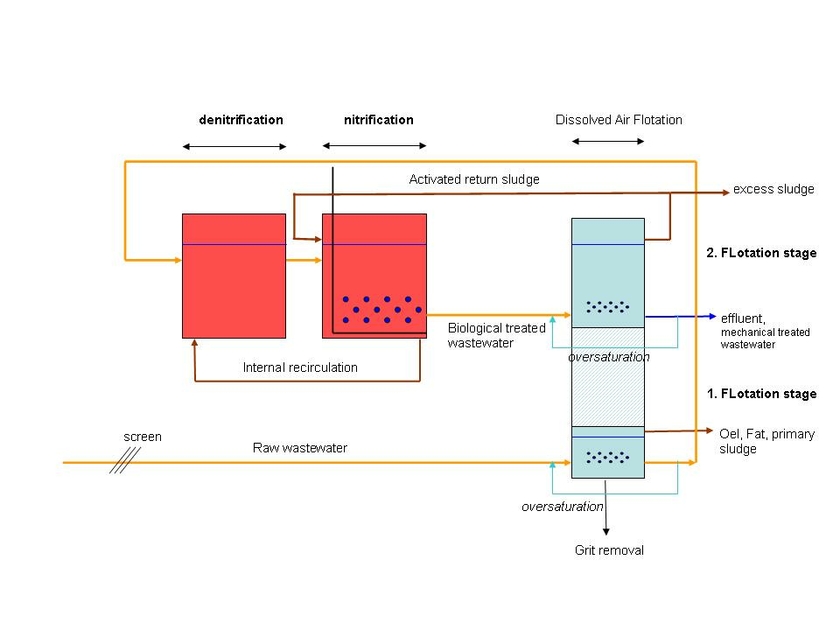
Profile of the complete modular flotation plant
Project objectives:
Research on the behavior of the biology and morphology of the activated sludge (thickening, N-elimination, bulking sludge).
Optimization of energy and chemical use (flocculation aid and coagulant).
Behavior of the flotation process during temporary high hydraulic loads (intermediate storage, sludge thickening).
One of the further targets of HydroNET is to develop a network of small wastewater treatment plants which can be controlled and monitored from a central station.
The idea is to develop a modular concept which allows en efficient and economic delivery and installation of the whole treatment module. The simple construction and the space saving design are in particular interesting for the chinese and indian market.
The CTI-project is realized by the company Krofta Waters International (KWI Corp. AG) in collaboration with the university of applied science Ticino (SUPSI) and Eawag Dübendorf.
