Department Environmental Chemistry
EXPOZOL
The EXPOZOL project was conducted at Eawag between September 2019 and October 2019 under the funding of the European Union (Horizon 2020, MSCA, Grant, 744052).
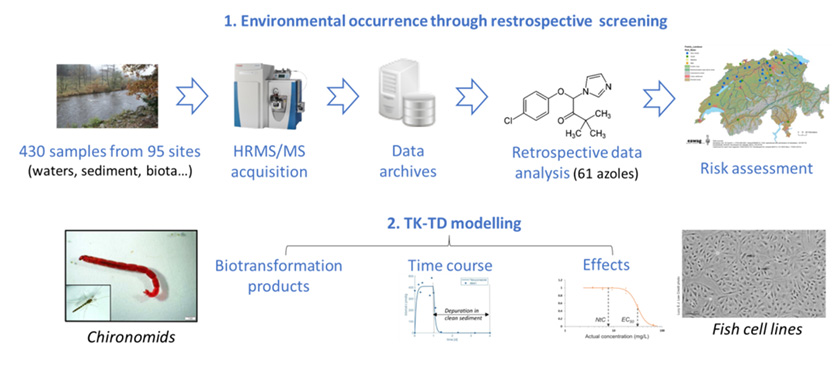
This project aimed gaining knowledge on the occurrence of antifungal azoles in aquatic ecosystems, their fate into aquatic organisms and associated effect(s) in order to improve their environmental risk assessment.
Overall, our results highlight that antifungal azoles are widely distributed in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. In particular, we showed that biota from different trophic levels are actually exposed to these chemicals. Thus, risk quotient calculations revealed risk especially if some of the investigated rivers and streams are used for drinking water production (Creusot et al. 2020). In addition, through toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic experiments, we confirmed the ability of aquatic organisms to bioaccumulate and biotransform antifungal azoles that can trigger adverse effect on these organisms (lethality, growth reduction).
Beyond the specific case of antifungal azole, our investigations showed clearly that the retrospective analysis of HRMS/MS data can improve the current knowledge on exposure and the related risks to chemicals of emerging concern, and can be effectively employed for such purposes in the future.
Publications
Posters and communications
Creusot N. and Hollender J. Researching the risk posed by antifungal azoles to aquatic ecosystems. https://cordis.europa.eu/article/id/415771-researching-the-risk-posed-by-antifungal-azoles-to-aquatic-ecosystems
Nicolas Creusot, Kristin Schirmer, Gayathri Jaikumar, Juliane Hollender. Biotransformation of antifungal azoles in rainbow trout cell lines (Poster). EUSSAT 2019 in Linz (Austria) in October 2019
Nicolas Creusot, Marie Lefranc, Carmen Casado-Martinez, Juliane Hollender
Toxicokinetic and Toxicodynamic modelling of the fungicide tebuconazole in the benthic organism Chironomus riparius. (Poster). SETAC Europe in Helsinki (Finland) in Mai 2019
Nicolas Creusot, Kristina Huba, Benoit J.D. Ferrari, Nathalie Chèvre, Juliane Hollender
Identification of bioaccumulative organic contaminants along the aquatic foodweb using high-resolution mass spectrometry (Poster). SETAC Europe in Helsinki (Finland) in Mai 2019 Oral Communication
Nicolas Creusot, Carmen Casado-Martinez, Aurea Chiaia-Hernandez, Benoit J.D. Ferrari, Stephan Fischer, Qiuguo Fu, Nicole Munz, Heinz Singer, Simon Spycher, Barbara Spycher, Christian Stamm, Ahmed Tlili, Irene Wittmer, Juliane Hollender. Towards better exposure assessment of antifungal azoles (Poster Corner). SETAC Europe in Rome (Italia) in Mai 2018






